
For decades, operations and technology leaders have been sold a compelling vision of inventory management automation. The pitch was that a sophisticated automated inventory management software package would eliminate manual effort, grant perfect visibility, and optimize stock levels, turning inventory from a liability into a finely tuned strategic asset. So, companies invested millions in advanced automated inventory management systems.
And yet, what is the reality in most large enterprises today? The warehouse and supply chain teams are still drowning in spreadsheets, emails, and manual data entry. The “automation” we bought is, for the most part, a fancy dashboard. It can tell us what our inventory levels are, but it does very little to automate the actual work of managing that inventory. The system can flag a low stock level, but it can’t autonomously execute the complex process required to replenish it. This is the great deception of traditional inventory management automation: we have been sold a system of record, not a system of action.
To understand why your current automated inventory system is failing, you have to look beyond the dashboard and see the invisible web of manual processes that your team performs every single day. The true source of inefficiency is not in counting stock; it’s in the gaps between your systems.
Consider the “simple” process of replenishing a part when stock runs low. An effective automating inventory management strategy must handle this entire workflow:
This is not an automated process. It is a series of manual tasks held together by human effort. This is the core problem that traditional inventory management automation was never designed to solve. This is where the real inventory control system benefits are being lost.
To truly conquer this complexity, leaders need a new class of technology. Agentic AI represents a fundamental paradigm shift for inventory management automation. It moves beyond dashboards and rigid bots to provide an intelligent engine that can execute entire end-to-end business processes, based on instructions provided in plain English.
Instead of just flagging a low stock level, an AI agent can be instructed to handle the entire workflow. A supply chain manager, without writing any code, can define the process:
“When inventory for Part #XYZ falls below 50 units, create a purchase order for 100 units from our primary supplier, Acme Corp. Email the PO and monitor their response for an order confirmation and ETA. Once confirmed, update the expected delivery date in our inventory system and notify the receiving department.”
The AI agent then uses its reasoning capabilities to navigate the different applications—the inventory system, the ERP, the email client—to get the job done. Crucially, it’s built for the real world. When an exception occurs—the vendor emails back that the part is on backorder—the agent doesn’t just fail. It can be taught to understand the email’s context and automatically initiate a PO with a secondary supplier, or to flag the exception for human review. This creates an automated inventory control system that is not just automated, but truly autonomous and resilient.
Kognitos is the industry’s first neurosymbolic AI platform, purpose-built to deliver this new, intelligent model of automation. Kognitos is not another dashboard or a better bot. It is a comprehensive platform that automates your most critical and complex operational processes using plain English.
The power of Kognitos lies in its unique neurosymbolic architecture. This technology combines the language understanding of modern AI with the logical precision required for enterprise-grade operations. This is non-negotiable for managing critical assets. It means every action the AI takes, from issuing a PO to approving an invoice, is grounded in verifiable logic, is fully auditable, and is completely free from the risk of AI “hallucinations.” This provides the governance and control that CIOs and CFOs demand from their automated inventory management software.
With Kognitos, you can finally achieve true inventory management automation:
Empower Your Operations Team: Your supply chain and inventory experts are the ones who know the process best. Kognitos allows them to build, manage, and adapt automations themselves, without waiting on IT. You can explore many inventory management system examples on our site to see this in action.
When you move from task automation to process automation, the inventory management system advantages become strategic, not just operational.
For large enterprises, the challenge of managing risk isn’t static; it’s a dynamic, ever-evolving landscape. Traditional methods of risk identification and mitigation, often reliant on manual checks and fragmented tools, simply can’t keep pace with the speed and complexity of today’s global operations. What’s needed is a transformative approach: one that leverages intelligent, autonomous systems for automated risk assessment. This shift moves beyond basic automation, leading to continuous identification, evaluation, and response to threats across the entire organization.
The objective isn’t merely to reduce human effort; it’s about building an enterprise-grade AI framework that ensures continuous compliance, significantly reduces financial exposure, and provides real-time visibility into an evolving risk landscape. This article will explore how organizations can achieve this by embracing advanced AI, particularly focusing on how some platforms empower proactive, resilient risk management frameworks through natural language process automation.
Modern enterprises face a multitude of risks, from cyber threats and regulatory non-compliance to supply chain disruptions and financial fraud. The sheer volume of data, coupled with intricate interdependencies across business units, makes comprehensive risk management a formidable task. Relying on periodic audits or siloed departmental efforts creates blind spots and leaves organizations vulnerable.
Effective risk management today demands a continuous, integrated approach. It requires the ability to sift through vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, identify subtle anomalies, predict potential failures, and trigger immediate, intelligent responses. This is where the power of an intelligent automated risk assessment platform becomes indispensable.
Automated risk assessment employs artificial intelligence and natural language processing to continuously identify, evaluate, and prioritize potential threats and vulnerabilities within an organization’s operations, financial systems, and compliance frameworks. Unlike manual methods, it leverages intelligent automation to process vast amounts of data, providing real-time insights and proactive risk mitigation strategies.
This goes beyond simple rule-based automation. True automated risk assessment involves sophisticated AI reasoning that can understand context, learn from historical data, and even handle exceptions intelligently. It’s about building systems that can think and adapt, not just follow predefined scripts. For instance, in finance, this could mean an AI system automatically flagging unusual transaction patterns indicative of fraud, or in operations, predicting equipment failure based on sensor data and maintenance logs. The goal is to move from reactive crisis management to proactive risk anticipation, greatly enhancing organizational resilience.
Kognitos empowers automated risk assessment through:
By focusing on natural language process automation and intelligent exception handling, Kognitos automates the underlying, interconnected processes of risk assessment. This makes it distinct from rigid, programming-dependent solutions, ensuring that your automated risk assessment tools are both powerful and flexible.
Implementing automated risk assessment with Kognitos involves a strategic approach that leverages its unique capabilities:
| Step | Description | The Kognitos Advantage |
| 1. Define Scope and Objectives | Clearly identify the specific risk areas and processes targeted for automation. | Business users define this directly in natural language, ensuring alignment with organizational goals. |
| 2. Integrate Data Sources | Connect to all relevant data, both structured and unstructured, across the enterprise. | Supports any data type, from enterprise applications to documents and emails, providing a unified view for automated risk assessment. |
| 3. Design Automated Workflows | Map out the “if-then” logic for identifying risks, assessing their impact, and triggering responses. | English as code enables rapid design and iteration by business and IT teams working collaboratively. Pre-built workflows can be deployed or customized. |
| 4. Implement Intelligent Exception Handling | Establish clear protocols for human intervention when AI encounters ambiguities or new scenarios. | The Guidance Center ensures human-in-the-loop validation, which the Process Refinement Engine learns from for continuous improvement. |
| 5. Continuous Monitoring and Refinement | Maintain ongoing oversight of the automated processes and adapt them as risk factors evolve. | Patented Process Refinement Engine and automatic agent regression testing ensure automations remain current and effective. |
These steps demonstrate how Kognitos enables organizations to go beyond basic task automation, moving towards truly intelligent automating risk management.
The adoption of an advanced platform for automated risk assessment yields significant advantages for large enterprises:
These benefits collectively contribute to a more resilient, agile, and secure enterprise. By embracing automated risk management, businesses can transform risk from a burden into a strategic advantage.
Achieving success with automated risk assessment involves adhering to several key practices:
These practices, when combined with the right platform, create a robust framework for automating risk management effectively.
The future of risk management is intelligent, proactive, and adaptive. It moves beyond traditional, reactive measures to embrace the full potential of AI-driven automated risk assessment. For large enterprises, this isn’t just about efficiency; it’s about competitive advantage and survival in an increasingly complex and unpredictable world.
Kognitos, with its unique blend of natural language process automation, neurosymbolic AI, comprehensive governance, and a patented Process Refinement Engine, is positioned to redefine how organizations approach risk. It empowers business users, brings IT and business onto the same page, and ensures that risk management frameworks are not just robust, but also continuously learning and evolving. By choosing the right platform, enterprises can transition from merely reacting to threats to intelligently anticipating and mitigating them, building an unparalleled level of organizational resilience.
How financial leaders can navigate the rush to adopt AI and find the ideal solution for their business.
By Binny Gill, CEO of Kognitos
Enterprises across every industry are eagerly jumping on the AI bandwagon, driven by the promise of unparalleled efficiency, innovation, and a supposed competitive edge. However, the journey from ambition to real-world implementation is fraught with significant challenges, especially for the banking and finance sectors.
While businesses initially embraced AI with enthusiasm, there is now growing skepticism about the tangible ROI that AI can deliver. Major media outlets are questioning why seven leading tech giants are doubting the technology’s long-term investment viability; while others are asking, “Has the AI bubble burst?” Some hedge funds have even warned investors to be skeptical of companies like Nvidia, while others suggest Big Tech is struggling to convince Wall Street that AI investments will bring real returns altogether.
Recent insights from Gartner underscore these challenges, predicting that 30 percent of generative AI projects will be abandoned after the proof-of-concept stage by 2025. Major financial institutions like Goldman Sachs echoed this cautionary stance, recently releasing a report downplaying the so-called “AI gold rush,” describing the promised ROI from Silicon Valley as little more than snake oil—a sentiment shared by Barclays and Sequoia Capital.
So, what’s the verdict? Is AI just another overhyped trend destined to fade away? Not quite. There’s more to the story than the doubters suggest.
At the enterprise level, scaling AI solutions, ensuring security and ethical compliance, and managing increasing costs—particularly those associated with training large language models (LLMs)—present challenges. But the release of OpenAI’s GPT-4o mini has reignited discussions on the long-term viability of AI adoption, spotlighting a shift towards smaller, specialized LLMs.
Are these specialized AIs more valuable than general-purpose ones? As companies navigate AI’s vast potential, many remain unsure of the most effective use cases, often realizing they don’t know what they don’t know.
For financial leaders, the potential benefits of generative AI extend beyond the hype. Financial processes that are integral across organizations—like Procure to Pay (P2P), Order to Cash (O2C), and Record to Report (R2R)—can gain significantly from these advanced capabilities. While some may be skeptical of yet another automation promise, it is essential to take a holistic view.
Embracing AI’s potential streamlines workflows, fosters innovation, and helps maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market. For financial leaders, this all begs one major question: How can we make it work for our business?
Effective evaluation of smaller AI solutions requires asking the right questions. By zeroing in on these crucial inquiries, organizations can meticulously assess AI models and vendors and thoroughly address concerns about the safety and efficacy of AI technologies. This approach ensures that the solutions they choose are not only trustworthy but also perfectly tailored to their specific needs and risk profiles.
Ensure the AI vendor provides straightforward descriptions of all automated processes. This transparency helps stakeholders understand the AI system, verify compliance with standards, and build trust in the vendor’s accountability.
Confirm the vendor’s ability to tailor LLMs and cloud setups to your specific requirements. Customization enhances performance, security, and compliance, aligning the AI solution with your strategic goals.
Check if the AI system allows for human control and review. This is essential for ensuring accuracy, reliability, and ethical use, helping to prevent errors and biases while maintaining system integrity.
Ensure the vendor supports both deterministic (fact-based) and generative (intuitive) AI processes. This combination leverages accuracy and creativity, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency.
Confirm if the vendor uses your data for training models beyond your control. Protecting your data ensures privacy, safeguards intellectual property, and maintains compliance with data protection regulations.
Traditional automation has hit a wall when it comes to the complexity of financial workflows. But, without all the hyperbole, AI is a real game-changer. It can handle tasks previously deemed impossible, turbocharging productivity and slashing costs across financial operations. Unlike rigid, high-maintenance predecessors, AI adapts, learns, and evolves.
Unlike earlier automation tools, AI’s adaptability and learning capabilities allow it to handle intricate, cross-functional processes. This flexibility, coupled with generative AI’s broad applications, positions AI as a transformative technology for the financial industry. Business leaders just need to know how to implement it.
Imagine workflows that seamlessly connect your entire organization, unlocking hidden value. Yes, there are challenges—transparency, accuracy, and privacy always are—but with careful scrutiny, these can be managed. By addressing these challenges and asking the right questions, financial institutions can unlock new opportunities to streamline operations, drive innovation, and maintain a competitive edge.
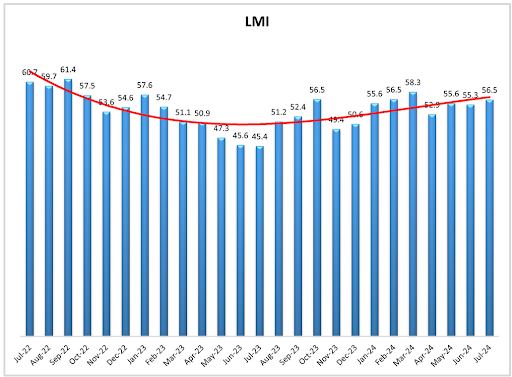
The past few years have been tough for logistics executives. Supply chain disruptions, excess inventory from the post-COVID boom, and rising inflation have all contributed to what’s been termed the “Freight Recession.” These factors, along with looming recession fears, have made long-term decision-making incredibly challenging. Even though 2024 has seen improvements with increased demand for freight and rail, the market remains below average, according to the Logistics Manager Index.
However, there is a silver lining. As the market begins to show signs of recovery, logistics executives are faced with a crucial question: How can they maintain low-cost structures while preparing their firms to seize opportunities when the market rebounds?
Many logistics companies are using this downturn as an opportunity to invest in AI. This strategic move aims to cut costs in the short term and enhance efficiency and capacity in the long run. This raises an intriguing question: Will the logistics leaders of tomorrow be shaped by the challenges of today’s down-market?
Amid the economic downturn, logistics firms are turning to AI to trim costs and maintain margins. With advancements in AI and NLP-backed technologies, businesses can now automate a broader range of processes without needing large developer teams. Traditionally, many logistics companies outsourced labor-intensive tasks like keying and matching documents such as Bills of Lading, pack slips, and commercial invoices with TMS or ERP systems. However, AI now enables firms to handle these tasks in-house without increasing headcount.
AI systems can receive customer documentation, extract necessary information from even poor-quality documents, create appropriate records in applications, and match or verify this data against other sources. In-house billing teams are flagged to handle specific exceptions and train the AI to manage similar situations in the future.
Bringing these services in-house not only optimizes costs temporarily but also gives logistics firms greater control over process improvements and creates a scalable solution. Unlike outsourcing, where firms must anticipate and pay for additional offshore workers to meet demand, AI systems are serverless and dynamically scalable. They scale on demand as transactions occur, offering executives infinite capacity to handle spikes in demand without overcommitting.
Discover how Kognitos manages exceptions without breaking automated processes:
Watch Now
In 2023, the American Trucking Association reported a shortage of over 80,000 drivers, creating an urgent need for trucking and logistics companies to hire and retain drivers and support staff throughout the value chain. A key to addressing this challenge is enhancing the driver and employee experience, making it positive and differentiated.
Traditionally, safety and quality teams spend significant time annually reviewing driver and warehouse team member certifications and documentation, including driver’s licenses, medical examiner’s certificates, training certificates, background checks, and motor vehicle records. This has been a major cost center, as the wide variety of document formats and unstructured data/images couldn’t be automated previously.
AI now enables these processes to be automated end-to-end, reducing the hours required to onboard or re-certify drivers. This decreases turnaround time, getting drivers on the road and driving revenue faster. Quality and safety improve as automation reduces errors and omissions.
In a down-market, the impact of faster onboarding is crucial. When market demand returns, improving the ability to scale quickly and avoiding bidding wars for talent by providing a positive company experience becomes essential.
Logistics executives are heavily investing in AI to prepare for capturing orders and new business when the market rebounds. In high-transaction sales, it’s crucial to maximize time spent hunting for new opportunities and minimize time on manual order entry or data searches. Traditionally, this required extensive sales support, contact centers, and order entry teams. As market demand increased, more support staff had to be hired. Errors, such as incorrectly typed information, could cause customer disruptions, damage relationships, and distract salespeople from their core responsibilities.
With AI, organizations can maintain a leaner staff and achieve faster cycle times in the order-to-cash (O2C) value chain. Manual entry steps in the sales process are automated, allowing sales reps to focus on new business and enhancing individual productivity. AI scales with sales, eliminating the need to hire additional support staff ahead of predicted sales volumes. Errors are reduced, leading to better customer and employee experiences.
Companies investing in AI during the downturn will be better prepared than their rivals to capture demand when the market rebounds. These nimble companies have not only trimmed costs but also implemented dynamic systems that enable them to scale without a proportional increase in employee count. More productive employees, focused on higher-value activities, will improve retention rates and customer experiences, creating significant differentiation. Retaining processes in-house, rather than outsourcing, will further boost quality and give logistics firms greater control over their operations.
Forward-thinking logistics leaders are using this crisis, including layoffs and disruptions, to position themselves for future success. By leveraging AI to optimize hiring, retention, process management, and order capturing, they are building a foundation for scalability and efficiency. Those who fail to adopt AI will find themselves struggling to keep up. The logistics leaders of tomorrow are being forged in today’s challenging market, and their success will be powered by AI.
Before delving into the specifics of Private AI, it’s important to understand the broader concept of Artificial Intelligence. AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions. This technology enables systems to learn, reason, solve problems, perceive, and even understand language. AI powers everything from virtual assistants to complex analytical engines that predict market trends or optimize supply chains. Its applications are vast, constantly evolving, and rapidly transforming every industry.
Private AI refers to an AI environment that is exclusively dedicated to a single organization. In this setup, AI models are trained, deployed, and managed using an organization’s proprietary data, with access strictly limited to that enterprise. The defining characteristic of Private AI is that sensitive data never leaves the organization’s control. It contrasts sharply with public AI services, where data might be processed or used by external providers.
The purpose of Private AI is to provide businesses, especially those in highly regulated sectors like banking, the full transformative power of AI without compromising data ownership, security, or confidentiality. For accounting, finance, and technology leaders, Private AI represents a strategic imperative for leveraging AI while mitigating significant risks.
Several core attributes define what truly makes an AI system private. These characteristics ensure that a Private AI model operates securely within an enterprise’s boundaries, protecting its most valuable asset: data. Understanding these attributes is crucial for any organization considering adopting this advanced approach.
Key elements that ensure an AI is private include:
These attributes collectively enable businesses to harness AI’s benefits without compromising data integrity or regulatory compliance.
Understanding the difference between public and Private AI is fundamental for making informed technology decisions. While both leverage AI capabilities, their operational models and implications for enterprise data differ significantly. This distinction defines their suitability for various business needs.
The choice between public and Private AI often hinges on an organization’s data sensitivity, regulatory requirements, and the need for customized, proprietary intelligence. Private artificial intelligence offers a pathway to leverage AI without compromising on core enterprise values.
The importance of Private AI for modern enterprises cannot be overstated. As AI becomes integral to business operations, the way data is handled and intellectual property is protected becomes a critical strategic differentiator. Private AI directly addresses these concerns, offering a secure foundation for AI adoption.
Its significance stems from several key factors:
These factors collectively underscore the strategic importance of Private AI in today’s data-driven economy.
Adopting a Private AI approach offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond mere data security, impacting operational efficiency, strategic decision-making, and financial prudence. These advantages make it a compelling choice for large enterprises.
Key benefits include:
These benefits demonstrate why Private artificial intelligence is becoming the preferred strategy for forward-thinking enterprises.
For enterprises seeking to harness the power of AI without compromising on data privacy, control, or security, Kognitos offers a unique and compelling solution for Private AI, by leveraging a neurosymbolic AI architecture designed for precision and governance, inherently supporting the principles of Private AI. This makes Kognitos a crucial tool that helps banks and other highly regulated entities in addressing their complex risks securely.
The platform empowers business users to automate complex processes using plain English. This innovative approach allows organizations to keep their sensitive data and processes entirely within their control, fostering a truly Private AI environment.
Through these differentiators, Kognitos provides an enterprise-grade, non-generic AI solution that inherently supports the secure, controlled, and private use of AI for mission-critical business automation. This makes Kognitos one of the leading Private AI companies enabling practical, secure AI adoption.
Successfully implementing Private AI requires careful planning and strategic execution. Organizations must consider several factors to ensure their Private AI model is effective, secure, and compliant. These considerations guide the path to leveraging Private artificial intelligence effectively.
Key implementation considerations include:
Addressing these considerations thoughtfully ensures a smooth and secure transition to Private AI.
The future of enterprise intelligence is undeniably anchored in Private AI. As data privacy concerns escalate and regulatory landscapes tighten, the ability to harness AI’s power while maintaining absolute control over proprietary information becomes non-negotiable. The importance of Private AI will continue to grow exponentially for businesses across all sectors.
Kognitos is at the forefront of this crucial shift, offering a platform that inherently supports a Private AI model for enterprise automation. By combining neurosymbolic AI with natural language processing, Kognitos empowers organizations—including banks and other Fortune 1000 companies—to build intelligent automations securely and privately. This strategic move enables businesses to unlock AI’s full potential, ensuring data integrity, mitigating risks, and securing a sustainable competitive advantage in an increasingly data-driven world.
The backbone of effective modern enterprises rests on meticulously defined and masterfully executed processes. For decades, organizations have pursued strategies to refine their workflows, magnify output, and pare down human error. This relentless pursuit birthed Business Process Management (BPM), a structured discipline that has fundamentally reshaped how enterprises operate. For accounting, finance, and technology leaders in prominent corporations, an acute understanding of BPM’s nuances stands as a cornerstone for strategic foresight and achieving dynamic organizational agility.
While conventional automation approaches, often bound by rigid rules, once held sway, contemporary breakthroughs, particularly in artificial intelligence, are now fundamentally altering the very nature of Business Process Management. This exposition aims to deliver a thorough dissection of BPM, tracing its historical trajectory, outlining its core constituents, detailing its diverse categories, and illuminating its continuous cycle. We’ll examine BPM’s operational mechanics, its widespread applicability across varied industries, and how it persistently morphs operational paradigms, championing superior productivity and strategic nimbleness.
The impulse for optimizing processes isn’t a fresh idea. Its roots delve into the Industrial Revolution, where visionaries like Frederick Winslow Taylor and Henry Ford pioneered systematic task standardization and assembly line optimization for peak efficiency. Later, the mid-20th century saw quality methodologies, notably Total Quality Management (TQM) and Six Sigma, further underscore process refinement as a means to curtail defects and mitigate waste.
However, the formal discipline known as Business Process Management solidified its identity in the late 20th and early 21st centuries. It arose in direct response to the escalating intricacies of modern businesses and the swift advancement of information technology. Unlike earlier methodologies that frequently targeted isolated tasks or single departmental functions, BPM adopted an expansive, end-to-end perspective on business processes. This holistic view aimed to manage processes not merely as a string of activities, but as a critical strategic asset directly influencing enterprise performance and client satisfaction.
The inaugural wave of BPM tools often centered on graphical process mapping, rudimentary workflow automation, and basic performance analytics. These pioneering BPM tools empowered companies to visually articulate processes and automate straightforward, rule-driven workflows, thereby laying a crucial foundation for more sophisticated business process management software. This historical lens reveals BPM as an ongoing revolution in the execution of work.
Business Process Management (BPM) constitutes a systematic discipline that leverages various methods to uncover, visually represent, scrutinize, quantify, enhance, and ultimately optimize entire business processes. Its central ambition is to elevate organizational performance, efficiency, and flexibility by meticulously aligning processes with overarching strategic objectives. BPM is not a singular, discrete project, but rather an unending cycle of refinement, fixating on the inherent flow of work throughout an organization.
Within this context, a process denotes a specific sequence of interconnected activities designed to yield a particular outcome. For instance, the onboarding of a new customer, the handling of an invoice, or the approval of a loan application all exemplify business processes. Effective Business Process Management endeavors to ensure these processes function with peak efficiency, unwavering compliance, and maximum adaptability. This systematic approach frequently incorporates the deployment of specialized BPM tools to aid each phase of the journey.
The Business Process Management lifecycle is far from a linear journey; instead, it epitomizes a continuous, iterative circuit of enhancement. A thorough comprehension of these distinct phases proves paramount for successful BPM implementation.
This cyclical methodology guarantees that processes remain exquisitely tuned and perfectly aligned with evolving enterprise demands, thereby consistently delivering substantial business process management benefits.
Business Process Management (BPM) broadly segments into various categories, each distinguished by its primary operational emphasis. Modern BPM solutions frequently integrate elements from these categories, increasingly harnessing artificial intelligence for heightened intelligence and adaptability.
Understanding these distinctions empowers organizations to select the most suitable BPM tools and strategies for their unique operational requirements, ensuring they realize maximum business process management benefits.
The strategic adoption of Business Process Management bestows profound advantages upon organizations across all sectors. These business process management benefits transcend mere financial savings, permeating every dimension of operational excellence.
These compelling business process management benefits unequivocally demonstrate why BPM remains a foundational discipline for any competitive enterprise.
While Business Process Management has historically leaned on various BPM tools for its automation aspects, the emergence of advanced artificial intelligence has unlocked fundamentally new realms of possibility. Conventional business process management software often mandated complex coding or intricate visual workflows, largely confining process ownership and modification to IT departments. Kognitos is now fundamentally disrupting this established model, offering a secure AI automation platform that truly revolutionizes business process automation.
Kognitos is distinct from Robotic Process Automation (RPA); it’s not a mere low-code/no-code tool in the traditional sense, nor is it simply a generic AI platform. Instead, Kognitos delivers natural language process automation. This means that business users—the leaders in accounting, finance, and operations who possess the deepest understanding of their day-to-day processes—can directly define, automate, and manage complex workflows using plain English.
Kognitos invigorates a business process automation workflow by:
This groundbreaking approach positions Kognitos as an unparalleled partner for organizations aspiring to elevate their Business Process Management initiatives, ushering in truly intelligent automation that is flexible, infinitely scalable, and broadly accessible across the entire enterprise.
The trajectory of Business Process Management is unequivocally one of continuous evolution, increasingly integrated with advanced artificial intelligence and intelligent automation. The future of BPM will be defined by:
The future of Business Process Management is poised to deliver unprecedented levels of operational agility, profound efficiency, and breakthrough innovation, ensuring organizations remain acutely competitive in a relentlessly evolving global landscape.
Large organizations rely on enterprise applications as the fundamental infrastructure for modern business operations. These sophisticated software systems transcend mere utility; they serve as the digital nervous system, streamlining intricate processes, boosting efficiency, and facilitating seamless collaboration across vast, often geographically dispersed, enterprises. For leaders in finance, accounting, and technology, a deep understanding of enterprise applications is vital for strategic planning and unlocking scalable growth.
This article will clarify what enterprise applications truly entail, explore their indispensable significance, categorize their various forms, and highlight how advanced automation solutions like Kognitos integrate with and amplify their positive business impact.
Enterprise applications are extensive, intricate software systems specifically engineered to support critical business functions and operations within large organizations. Unlike typical consumer-facing apps or smaller business tools, enterprise applications software is constructed to manage immense volumes of data, accommodate thousands of users, and integrate with multiple existing systems. Their primary purpose is to address enterprise-level challenges, such as overseeing supply chains, processing financial transactions, managing customer relationships, or optimizing human resources.
These powerful solutions frequently act as the core digital infrastructure of a company, ensuring that various departments can operate efficiently together, share data securely, and uphold consistent operational benchmarks. Whether it’s an enterprise applications platform for resource planning or a specialized tool for enterprise applications banking, their objective is to advance the overarching strategic goals of the business.
In today’s fiercely competitive environment, the strategic value of robust enterprise applications is undeniable. They are indispensable for several crucial reasons:
Effectively leveraging enterprise applications isn’t solely about adopting new technology; it’s about constructing an organization that is resilient, adaptable, and prepared for future demands.
The landscape of enterprise applications is broad, featuring solutions customized for various business functions. Here are some of the most common enterprise application examples:
Implementing a strategically chosen enterprise applications platform yields transformative advantages:
For enterprise applications to deliver their complete potential, effective enterprise applications integration is paramount. In large organizations, various systems (ERP, CRM, SCM, custom applications) often operate in isolation. Seamless integration ensures that data flows freely between these systems, providing a unified operational and customer view. This frequently involves constructing an enterprise application architecture that supports interoperability, scalability, and resilience.
Key aspects of integration include:
A well-designed enterprise application architecture supports not only current operational needs but also future expansion and the adoption of new technologies, including advanced automation.
While enterprise applications provide the essential structural framework, many processes within them still involve manual steps, data inconsistencies, or human decision points that can slow down operations. This is precisely where intelligent automation, particularly through natural language processing, emerges as a game-changer for enterprise app solutions.
Traditional automation approaches, such as RPA, often prove fragile when processes deviate from rigid rules or involve unstructured data within enterprise applications software. Kognitos offers a fundamentally different methodology. Instead of merely replicating mouse clicks and keystrokes, Kognitos understands and executes business processes described in plain English. This implies that:
For example, consider vendor invoice reconciliation, a common process residing within an ERP system. While the ERP manages the data records, the matching, exception resolution (e.g., missing purchase orders, incorrect line items), and approval workflows can remain highly manual. Kognitos can connect to the ERP, interpret emails, extract unstructured invoice details, perform matching, flag discrepancies, and initiate approvals, all based on natural language instructions. This dramatically enhances the efficiency and accuracy of existing enterprise IT application processes, transforming them into truly intelligent workflows.
Despite the immense advantages, implementing and managing enterprise app solutions presents its own set of challenges:
Addressing these challenges demands meticulous planning, strong project leadership, and a clear understanding of the business’s unique requirements.
The future of enterprise application solutions is undeniably intertwined with advanced AI and cutting-edge automation. We can anticipate:
The evolution of enterprise applications will continue to drive digital transformation, enabling businesses to become more agile, intelligent, and competitive.
Contracts form the very bedrock of all business relationships today, meticulously governing everything from vendor alliances to client commitments. Yet, the traditional stewardship of these pivotal documents—fraught with manual drafting, arduous negotiation loops, paper-based approvals, and fragmented tracking—often breeds debilitating inefficiency, introduces cascading errors, and exposes organizations to unnecessary risks. It is precisely within this critical operational arena that contract automation decisively solidifies its position as an undeniable transformative imperative. For leaders in accounting, finance, and technology within prominent corporations, discerning the profound impact of contract automation on operational velocity and comprehensive risk mitigation is absolutely indispensable.
This article deep dives into concept of contract automation and the advanced capabilities inherent in cutting-edge contract management automation software. It will meticulously define contract automation, articulate its non-negotiable critical importance, detail its foundational functionalities and key features, and underscore the profound advantages garnered from adopting such intelligent solutions. These benefits encompass profoundly streamlining intricate contract lifecycle processes, markedly elevating operational efficiency, sharply curtailing costly errors, rigorously bolstering policy compliance, and effectively mitigating pervasive legal and financial risks. By sharply contrasting AI-powered automated methodologies with their antiquated manual counterparts and meticulously showcasing diverse applications across the entire contract lifecycle (e.g., precise creation, strategic negotiation, accelerated approval, and timely renewal), this content provides a comprehensive overview that deepens comprehension of this vital business practice. In essence, the article functions as an indispensable foundational resource for enterprises striving to embrace or optimize contract automation, championing its pivotal role in fostering significant time reclamation, amplified productivity, and robust legal and financial oversight.
Contract automation refers to the strategic deployment of advanced technological solutions to meticulously streamline and ultimately eliminate manual human interventions throughout the entire lifecycle of a contract, spanning from its initial drafting to its ultimate renewal or termination. It fundamentally transmutes historically cumbersome, document-centric processes into fluid, digital, and exceptionally efficient workflows.
This concept transcends the mere digitization of a standard contract template. Contract automation inherently involves:
An automated contract management solution is meticulously engineered to deliver a seamless, end-to-end digital experience, thereby eradicating the drudgery and inherent vulnerabilities of manual processing.
The strategic decision to automate contract management is driven by a compelling array of unassailable imperatives that directly impact an organization’s legal standing, fiscal resilience, and dynamic operational agility.
These compelling advantages unequivocally underscore why embracing an automated contract management approach is a non-negotiable strategic imperative for any contemporary enterprise.
A robust contract automation software typically boasts a comprehensive suite of contract automation features meticulously designed to streamline every phase of the contract lifecycle.
These contract automation features collectively form the formidable backbone of a truly transformative contract automation software.
To effectively automate contracts, organizations must adopt a strategic, phased approach, transcending mere digitization to embrace intelligent automation.
While numerous contract automation tools and conventional contract automation software solutions offer rudimentary digital contract management, Kognitos presents a fundamentally distinct and profoundly more powerful methodology. It is specifically engineered for the intricate, nuanced, and frequently exception-laden workflows endemic to contract management within sprawling enterprises.
The platform empowers sophisticated contract automation by:
By leveraging Kognitos, organizations can transcend traditional contract management automation approaches, ascending to a realm of truly intelligent, remarkably adaptive, and profoundly human-centric contract stewardship. This bestows unparalleled efficiency, significantly curtails risks, and cultivates formidable strategic agility.
The trajectory of Automating Contract Management points unequivocally towards even greater inherent intelligence, profound autonomy, and seamless integration across the enterprise. The future of contract management automation will be fundamentally characterized by:
By embracing intelligent automation platforms like Kognitos, businesses can truly transform their approach to Automating Contract Management, converting a traditionally resource-intensive function into a strategic asset for legal certainty, optimal financial performance, and accelerated business growth.
When most people think about AI in banking, they picture sophisticated chatbots on a bank’s website or personalized financial advice from a virtual assistant. These customer-facing AI applications in banking are undoubtedly valuable and have played a significant role in improving the customer experience. However, for leaders, the reality of modern banking is also defined by the unseen, back-office workflows that power it: loan processing, compliance reporting, vendor payments, and risk management. These internal tasks, while essential, are often a source of immense friction, cost, and risk.
This is the new frontier for AI in banking. While front-end applications have captured the public’s imagination, the most transformative and sustainable change is now coming from the intelligent automation of these back-office processes. A well-executed AI in banking industry strategy must be holistic, addressing not just customer interactions, but the operational burden that can stifle innovation and create unnecessary risk. This article will guide you through a new strategic approach to leveraging AI, one that moves beyond the customer-facing spotlight to create a truly unified and intelligent internal operation.
The sheer volume and complexity of administrative work in the banking sector is staggering. A single loan application might involve:
Managing this end-to-end workflow manually is not only inefficient but also prone to human error, which can have significant financial and compliance implications. The various systems—legacy mainframes, modern CRMs, and various third-party APIs—often do not communicate effectively. Teams are bogged down by repetitive data entry and communication tasks. While banking and AI are often discussed, this administrative part of the workflow is where the most significant friction lies. The key to unlocking the full potential of a bank is not just to improve customer interactions, but to intelligently orchestrate the entire process that supports it.
When we discuss the use of AI in banking, the focus is often on high-profile, customer-facing applications like personalization engines or fraud detection. These are valuable, but for an organization’s financial health and operational stability, a different kind of AI is needed.
A truly strategic approach to AI in banking recognizes that both are essential. Customer-facing AI can attract new clients, but operational AI can ensure the bank can serve them profitably and securely. It allows highly skilled and expensive professionals to focus on what they do best—building relationships and making strategic decisions—while intelligent agents handle the rest. This is a critical distinction that modern leaders must embrace to build a resilient and agile operation.
To understand the full potential of AI in banking, we must look at the specific back-office functions where it can have the greatest impact. Here are some key examples of artificial intelligence in banking:
The loan process is a time-consuming and document-intensive workflow that is ripe for automation.
Regulatory compliance is a major administrative burden. Manual compliance checks are time-consuming and prone to error.
The finance department in a bank handles a vast number of vendor invoices and payments.
The strategic deployment of AI in banking brings a host of measurable benefits that go far beyond simple cost reduction.
Empowered Employees: By offloading mundane tasks, AI in the banking industry empowers employees to take on more strategic roles, improving job satisfaction and reducing burnout.
The future of AI in banking is not a world without human professionals. It is a seamless, strategic partnership between intelligent AI agents and human expertise. The future of AI in banking will be defined by how well these two work together—AI handling the complex, end-to-end back-office processes, and humans providing the strategic direction and judgment.
As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of back-office and customer-facing systems will become more profound. The data from customer interactions will flow instantly into the administrative systems, triggering intelligent workflows that ensure a smooth and compliant operation. The ability to build and grow an AI-driven back-office is the key to unlocking true operational excellence and securing a competitive advantage in the future. The next wave of AI in banking will be defined by intelligent agents.
Information Technology (IT) operations form the foundation of the digital backbone of any large enterprise. The consistent delivery of services, maintenance of robust infrastructure, and seamless management of digital resources are paramount. This is where Automation in IT Operations asserts its indispensable value. What is automation in information technology? It is the strategic deployment of software, intelligent systems, and advanced workflows to manage and execute day-to-day IT tasks and processes with minimal human intervention. This proactive approach transforms manual, often repetitive, IT tasks into streamlined, efficient, and reliable digital procedures.
This article comprehensively explains Automation in IT Operations and its subset, IT process automation. It will detail precisely how AI and sophisticated automated workflows are fundamentally transforming daily IT management, moving beyond mere task execution to intelligent orchestration. For corporate leaders, understanding these advancements is crucial for optimizing IT spend, enhancing service delivery, and securing operational resilience.
Modern IT environments are characterized by escalating complexity, ballooning data volumes, and an ever-increasing demand for instantaneous service delivery. These factors collectively highlight the pressing needs for automation within IT operations. Manual processes, while once sufficient, now struggle to keep pace with the scale and speed required, leading to inefficiencies, errors, and increased operational risk.
Key needs for automation in IT include:
Addressing these fundamental needs for automation is critical for any IT operations system striving for optimal performance and efficiency.
The overarching objective guiding the implementation of automated solutions in the IT domain is profoundly strategic. What is the primary goal of automation in IT operations? It transcends mere task execution; its fundamental aim is to achieve unparalleled operational efficiency, unwavering reliability, and superior service delivery, thereby directly supporting core business objectives. It transforms the IT operations workflow from a reactive stance to a proactive, value-driven engine.
This primary goal encompasses:
Ultimately, the primary goal is to transform IT from a cost center into a strategic enabler for the entire enterprise, making it a truly resilient IT operations system.
Implementing comprehensive Automation in IT Operations yields a multitude of profound advantages that permeate every facet of an organization. The benefits of automating IT Operations extend far beyond mere cost savings, impacting reliability, security, compliance, and strategic innovation.
Key advantages include:
These compelling benefits of automating IT Operations underscore why it is a strategic imperative for any large enterprise.
The advent of Artificial Intelligence has profoundly transformed the landscape of Automation in IT Operations, elevating it from rule-based task execution to intelligent, adaptive orchestration. Is AI used in IT operations? Unquestionably, yes. AI is now integral to maximizing the impact of IT automation examples.
AI revolutionizes IT operations by:
The integration of AI makes IT automation smarter, more adaptive, and capable of addressing the complex, dynamic needs for automation in modern IT.
Virtually every facet of IT operations presents an opportunity for automation, leveraging IT process automation tools to streamline workflows. Identifying which IT operation processes can be automated is a strategic exercise for efficiency gains. These IT automation examples illustrate the breadth of possibilities.
Common IT operations workflow examples ripe for automation include:
These IT automation examples demonstrate how organizations can automate IT processes to achieve significant improvements in efficiency, reliability, and security across the entire IT operations system.
For large enterprises seeking to master Automation in IT Operations, Kognitos offers a fundamentally transformative approach. Its Agentic AI-powered platform inherently enables advanced IT operations workflow automation through its patented natural language AI and profound AI reasoning, making enterprise-grade automation natively accessible for orchestrating intelligent IT processes.
Kognitos empowers leaders to define and automate complex IT processes using plain English. This bridges the gap between understanding IT operational needs and actually automating them, allowing users closest to the work to articulate their requirements, and Kognitos uniquely translates that direct human insight into precise, auditable automation, making it a pivotal solution among IT process automation tools.
Kognitos streamlines the entire journey to intelligent Automation in IT Operations, making advanced enterprise IT automation practical, scalable, and inherently secure for large organizations.
Successfully implementing Automation in IT Operations requires a methodical approach. Understanding what are the steps to automate IT operations ensures a smooth transition and maximizes the benefits. This guides organizations from initial assessment to continuous optimization.
Following these steps allows organizations to effectively automate IT processes and achieve substantial operational gains.
Automation in IT Operations is no longer an optional enhancement; it is a fundamental pillar for achieving operational resilience and strategic advantage in the digital age. As enterprises continue to navigate increasing complexity and demand for always-on services, the ability to automate IT processes intelligently will define their success. The future points towards highly autonomous IT environments, driven by advanced IT process automation tools.